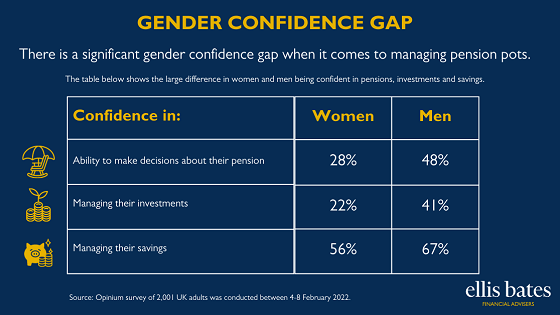
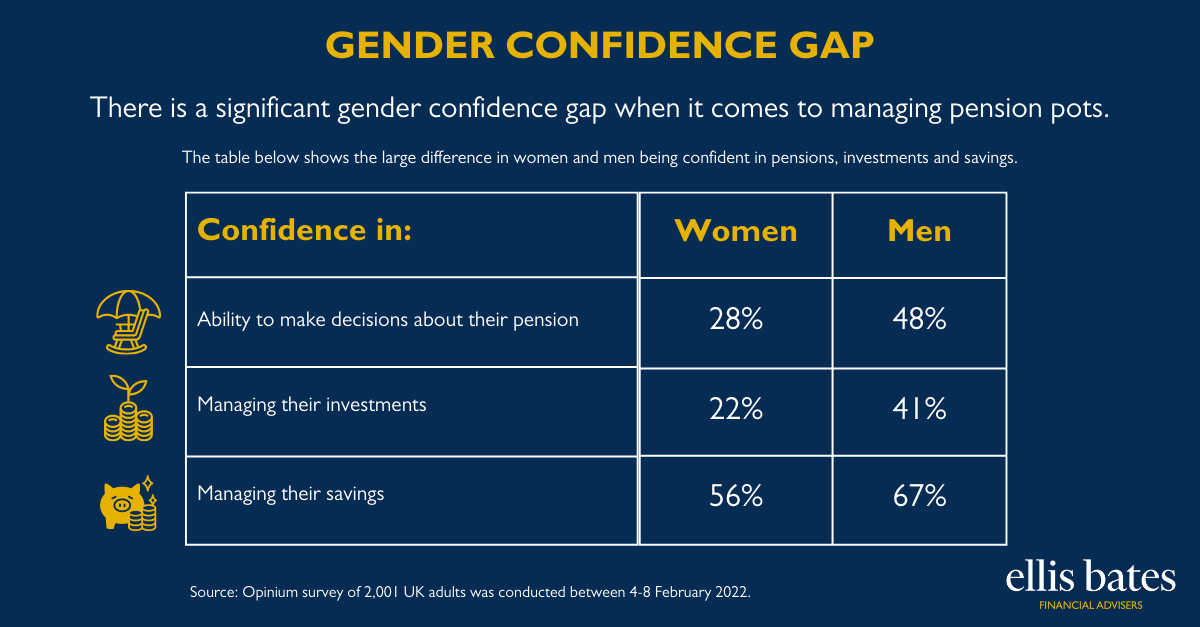
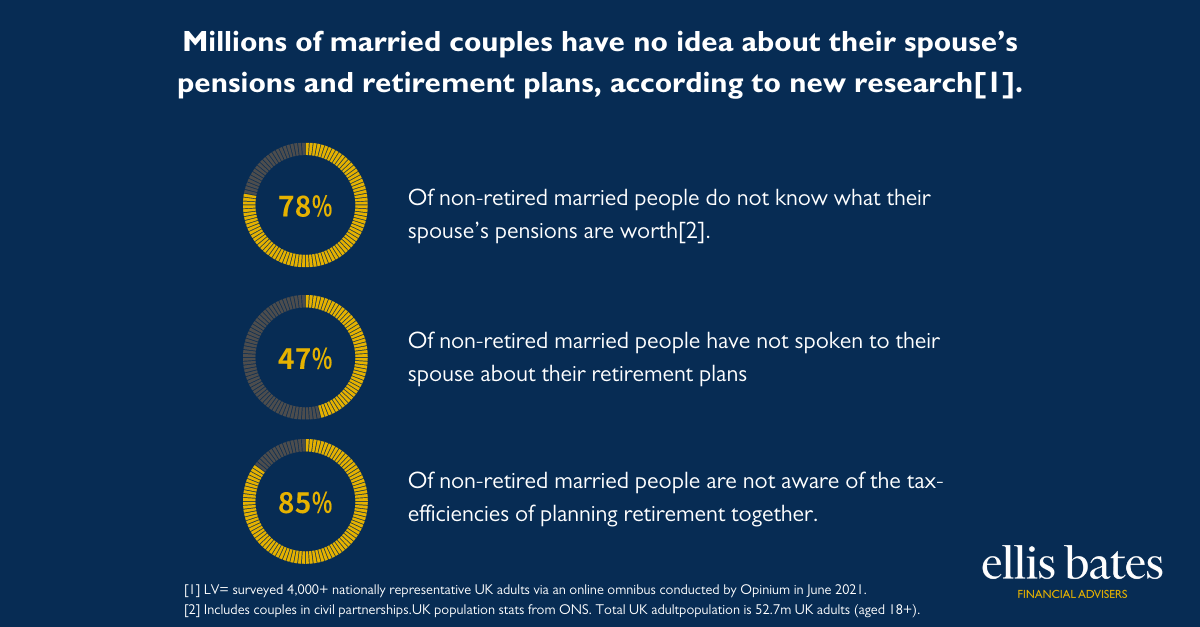
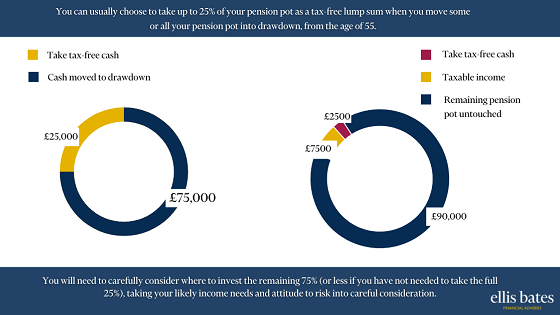
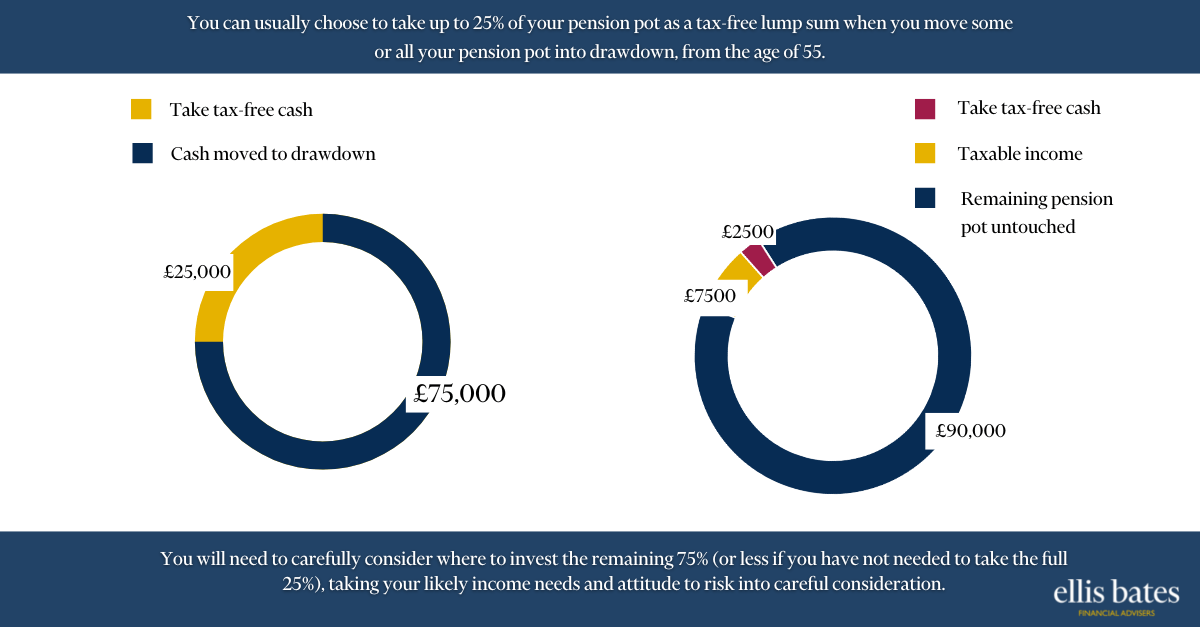
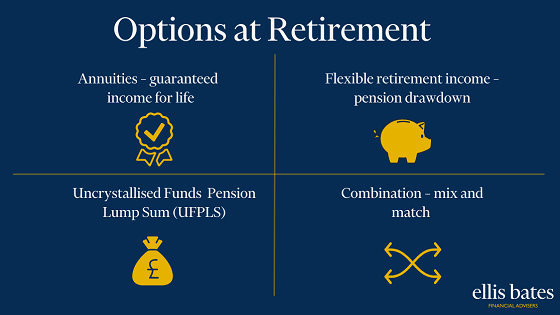
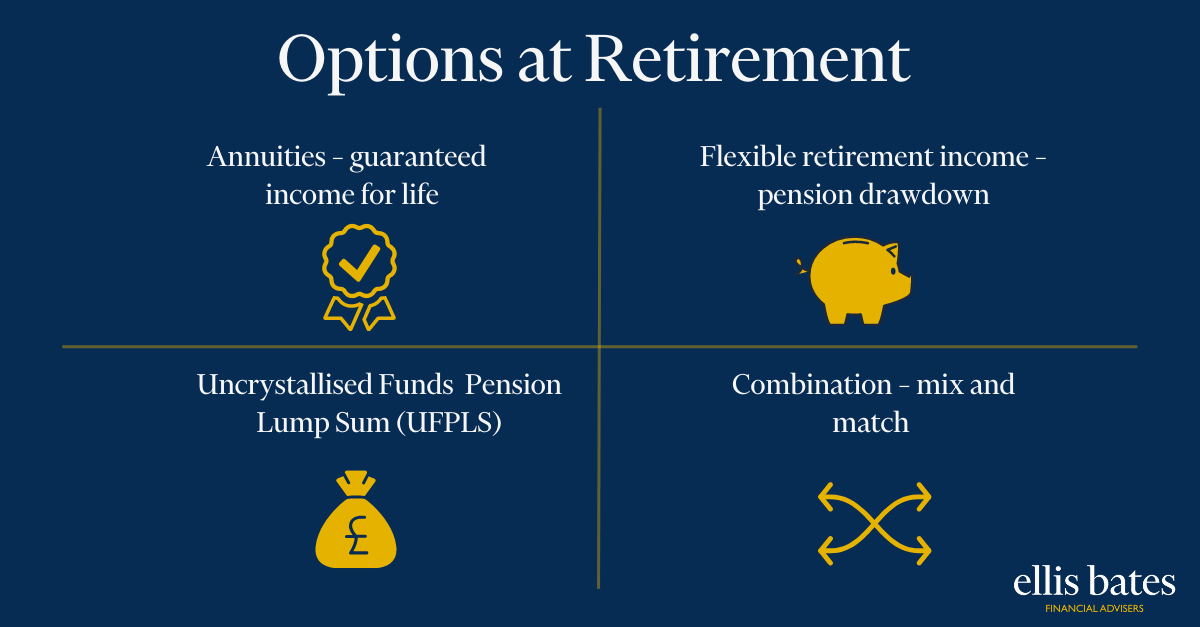
Financial Advice: Enhancing People’s Lives
https://www.ellisbates.com/wp-content/themes/osmosis/images/empty/thumbnail.jpg 150 150 Jess Easby Jess Easby https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/0e2a278e0eef1defdd7ee9d0ae7bb398?s=96&d=mm&r=gFinancial Adviser, Carol Lammy-Steele explains how she helped to enhance a client’s life by providing help and support to someone going through a divorce.